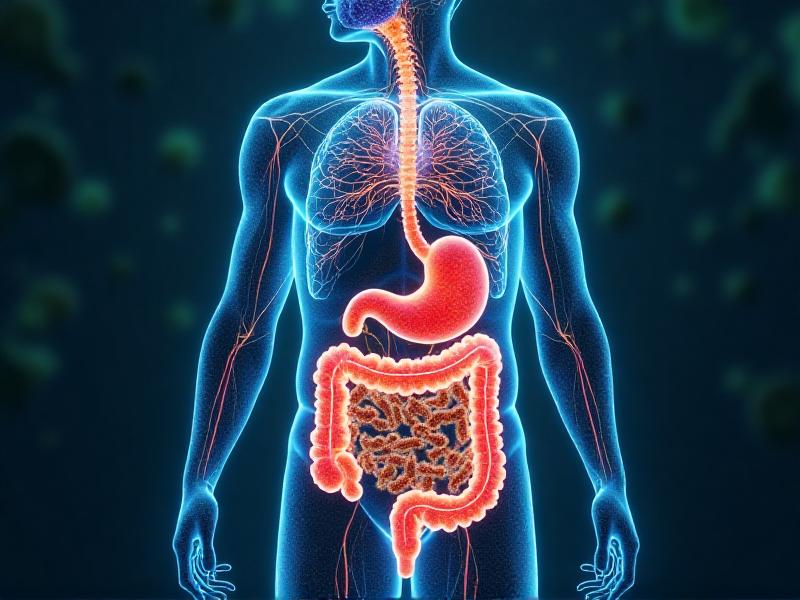
The Invisible Therapy: Probiotics and Mental Health Secrets
The Invisible Therapy: Probiotics and Mental Health Secrets
The Gut-Brain Connection: A Hidden Pathway to Mental Wellness
Linking the emotional and cognitive centres of the brain with peripheral intestine functions, the gut-brain axis is a sophisticated communication network. Recent research has uncovered that the gut microbiota, the community of microorganisms living in our digestive tracts, plays a crucial role in this connection. Probiotics, often referred to as "good bacteria," have been shown to influence this axis, potentially impacting mental health. Studies suggest that a balanced gut microbiome can help regulate mood, reduce anxiety, and even alleviate symptoms of depression. This invisible therapy is gaining traction as a complementary approach to traditional mental health treatments.
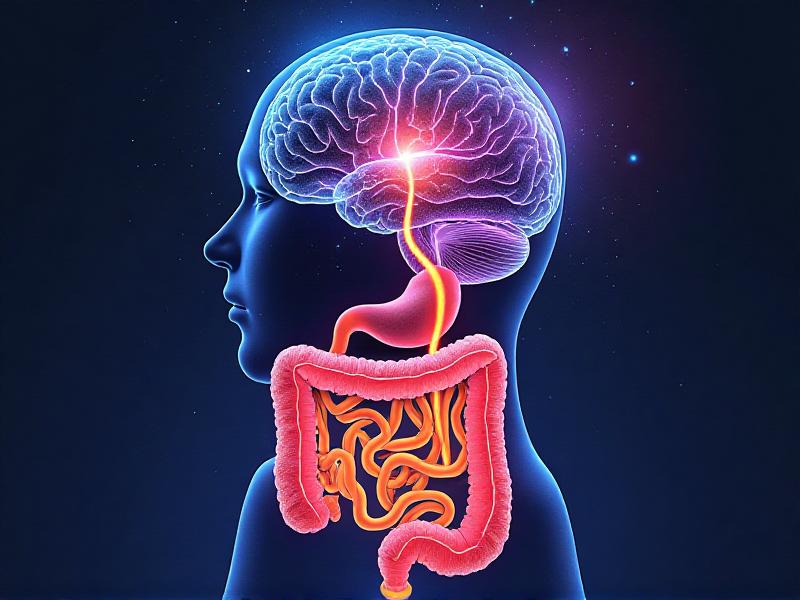
How Probiotics Influence Neurotransmitters
Neurotransmitters are chemical messengers that play a key role in regulating mood and behavior. Surprisingly, a significant portion of these neurotransmitters, such as serotonin and dopamine, are produced in the gut. Probiotics can influence the production and regulation of these chemicals, thereby affecting mental health. For instance, certain strains of Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium have been found to increase serotonin levels, which can help improve mood and reduce anxiety. This section delves into the science behind how probiotics interact with neurotransmitters and what this means for mental health treatment.
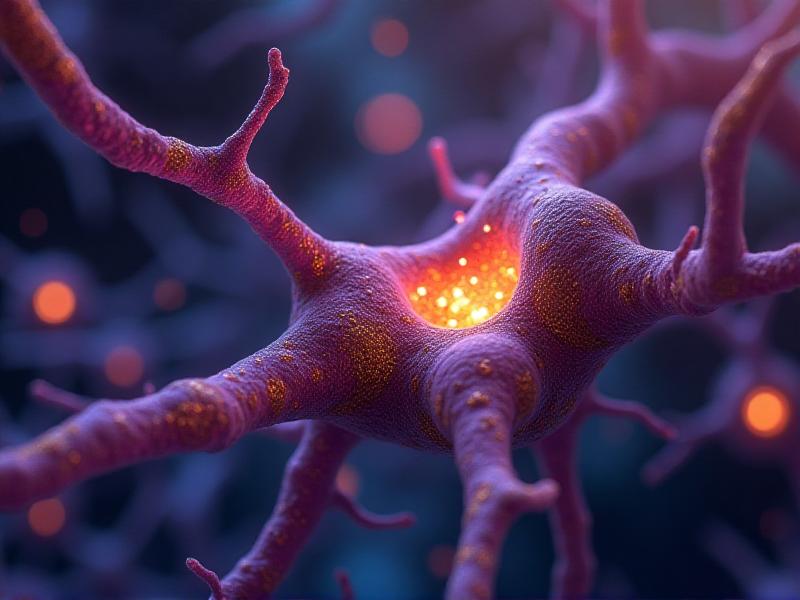
The Role of Probiotics in Stress Reduction
Chronic stress is a major contributor to mental health issues, and emerging evidence suggests that probiotics may help mitigate its effects. Stress can disrupt the balance of gut bacteria, leading to a condition known as dysbiosis, which is linked to anxiety and depression. Probiotics can help restore this balance, promoting a healthier gut environment. Additionally, some probiotics have been shown to reduce cortisol levels, the body's primary stress hormone. This section explores the mechanisms by which probiotics can help manage stress and improve overall mental well-being.

Probiotics and Anxiety: What the Research Says
Anxiety disorders are among the most common mental health conditions, affecting millions of people worldwide. Recent studies have begun to explore the potential of probiotics as a treatment option for anxiety. Research indicates that certain probiotic strains can reduce symptoms of anxiety by modulating the gut-brain axis. For example, a study published in the journal "Psychiatry Research" found that participants who took a specific probiotic blend experienced significant reductions in anxiety levels compared to those who took a placebo. This section reviews the latest research on probiotics and anxiety, offering insights into their potential benefits and limitations.

Depression and the Microbiome: A New Frontier
Depression is a multifaceted condition with various contributing factors, including genetics, environment, and lifestyle. Emerging research suggests that the gut microbiome may also play a significant role in the development and progression of depression. Probiotics have shown promise in alleviating depressive symptoms by restoring gut balance and reducing inflammation, which is often linked to depression. This section examines the relationship between the gut microbiome and depression, highlighting the potential of probiotics as a novel treatment approach.
Probiotics in Clinical Practice: What to Expect
As the evidence supporting the mental health benefits of probiotics grows, more healthcare providers are incorporating them into clinical practice. However, it's important to understand that probiotics are not a one-size-fits-all solution. Different strains and formulations may have varying effects, and individual responses can differ. This section provides an overview of what to expect when using probiotics for mental health, including potential side effects, dosage recommendations, and how to choose the right product. It also discusses the importance of consulting with a healthcare professional before starting any new treatment.

The Future of Probiotics in Mental Health Treatment
The field of psychobiotics, which focuses on the use of probiotics to treat mental health conditions, is still in its infancy but holds great promise. As research continues to uncover the intricate connections between the gut and the brain, the potential applications of probiotics in mental health treatment are expanding. Future studies may lead to the development of targeted probiotic therapies for specific conditions, offering new hope for those struggling with mental health issues. This section explores the future directions of probiotic research and what it could mean for the future of mental health care.

Incorporating Probiotics into Your Daily Routine
For those interested in exploring the mental health benefits of probiotics, incorporating them into your daily routine can be a simple yet effective step. Probiotics are available in various forms, including supplements, fermented foods, and beverages. This section offers practical tips on how to integrate probiotics into your diet, along with recommendations for maintaining a healthy gut microbiome. It also emphasizes the importance of a balanced diet and lifestyle in supporting overall mental well-being.

Conclusion: The Promise of Probiotics in Mental Health
The intersection of probiotics and mental health is a fascinating and rapidly evolving field. While more research is needed to fully understand the mechanisms and potential benefits, the existing evidence is promising. Probiotics offer a natural, non-invasive approach to supporting mental well-being, and their role in mental health treatment is likely to grow in the coming years. By understanding the gut-brain connection and making informed choices about probiotic use, individuals can take proactive steps toward improving their mental health and overall quality of life.